Finding aid aggregation
Overview of Aggregation Process
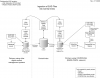
EAD files for all partners except BYU will be hosted as part of the Mountain West Digital Library (MWDL) system. All EAD files, including those from BYU, will be discoverable in the MWDL central index. The workflow for this process is illustrated in the diagram to the left and discussed below. All LSTA partners except BYU will follow the workflow on the right of the following diagram, while BYU will follow the workflow on the left.
For more information about the process described below, please contact Sandra McIntyre (mailto:sandra.mcintyre@utah.edu), Nathan Pugh (mailto:nathan.pugh@utah.edu), or Debbie Rakhsha (mailto:debbie.rakhsha@utah.edu) at the University of Utah Marriott Library. Information is available for the development team on a password-protected workspace within the Marriott Library's Sharepoint site.
Uploading EAD Files to CONTENTdm Hub
For all LSTA partners except BYU, EAD files will be uploaded to a CONTENTdm digital assets management system server. This involves two steps: (1) extracting the values in certain EAD elements and saving them as Dublin Core elements within a tab-delimited text file; and (2) using CONTENTdm's Acquisition Station to upload the EAD file and metadata to the Mountain West Digital Library hub server. Both steps can be done on multiple EAD files at a time for batch processing. A procedure is being developed by Cheryl Walters at USU.
An extraction script has been created to automate the first step. The EAD elements chosen for extraction and the Dublin Core fields they map to are given in the draft EAD-to-Dublin-Core Mapping Table.
Display of Individual EAD Files in CONTENTdm
For all LSTA partners except BYU, the display of EAD files will be within CONTENTdm.
As with all CONTENTdm collections, the CONTENTdm item viewer displays a header and footer of the partner's choice, typically with the partner's logo and other branding related to the EAD collection.
We have modified the CONTENTdm item viewer to bypass the usual display of Dublin Core metadata and instead to go directly to the display of the EAD file itself. The display is done using an XSL transform (XSLT), which uses an XSL stylesheet (template) to transform the XML in the EAD file into XHTML for viewing in a browser. For the purposes of the initial demonstrations, we used one of the stylesheet combinations given by the EAD 2002 Cookbook site. For production, we will tailor one of the stylesheet combinations (or create a new one) for the specific needs of the partners in this project. The stylesheet will transform each of the elements, required and optional, in the Best Practices Guidelines for this project.
Searching and Browsing
Institutional Search and Browse: Each CONTENTdm-based partner will be able to use standard CONTENTdm features to search and browse its own EAD files. In addition, partners may create special search and browse pages using CONTENTdm's Custom Query functions.
Central Search and Browse: The metadata from all uploaded EAD files will be harvested periodically and aggregated into the Mountain West Digital Library at http://mwdl.org. Search and browse pages within MWDL's interface will allow users to discover finding aids from all partners, or from any selected subset of the partners. In April, Sandra McIntyre and Nathan Pugh will be creating a search interface mockup for consideration by the LSTA partners.